Last Updated on 2021-08-02 by Admin
Notes
Options are contracts where you have the right but not the obligation to either buy (call ) or sell (put) financial instruments at the exercise (strike) price on or before a predetermined date.
Types
- American
-
- Can exercise the option any time up to the expiration date.
- Higher risk to the seller (writer).
- More expensive (premium) than the European type option.
- Options traded on the ASX are predominantly American type.
- European
-
- Can exercise the option only on the contract expiration date.
- Lower risk to the seller (writer).
- Less expensive (premium) than the American type option.
Strategies
- Vertical Bull Spread
- Call Bull Spread
- Vertical Bear Spread
- Put Bear Spread
- Straddle
-
- Long Straddle
- Short Straddle
- Strangle
-
- Long Strangle
- Short Strangle
- Barrier Option
- 1 Option Contract: 100 Shares
- Seller (Writer):
- Buyer (Taker):
- Call (Buy) Option: The right but not obligation to buy the financial instrument at the exercise (strike) price.
- Put (Sell) Option: The right but not obligation to sell the financial instrument at the exercise (strike) price.
- Premium:
-
- How much you pay for the contract.
- The level of risk is reflected in the premium of the option.
- Exercise (Strike) Price: The agreed price on the contract.
- Moneyness:
-
- In The Money (ITM): Profit
- The Strike Price of a CALL OPTION is below the market price.
- At The Money (ATM): Break-Even
- Out of The Money (OTM): Loss
- Deep In The Money: Large Gain
- An option that would lead to a large profit if it were exercised
- Covered Option: The writer owns stock to be able to fulfill the contract.
- Naked Call Option: The writer does not own stock to fulfill the contract which is underwritten by a third party.
- Option Contracts:
-
- Exchange Traded Options (ETOs)
- Over-The-Counter (OTC)
- Intrinsic Value
- Price Volatility
- Issued By:
- Issued To:
- Type of Security:
- Duration:
- Source:
- Market:
- Return:
- Principle:
- Liquidity:
- Risk Level:
Calculation
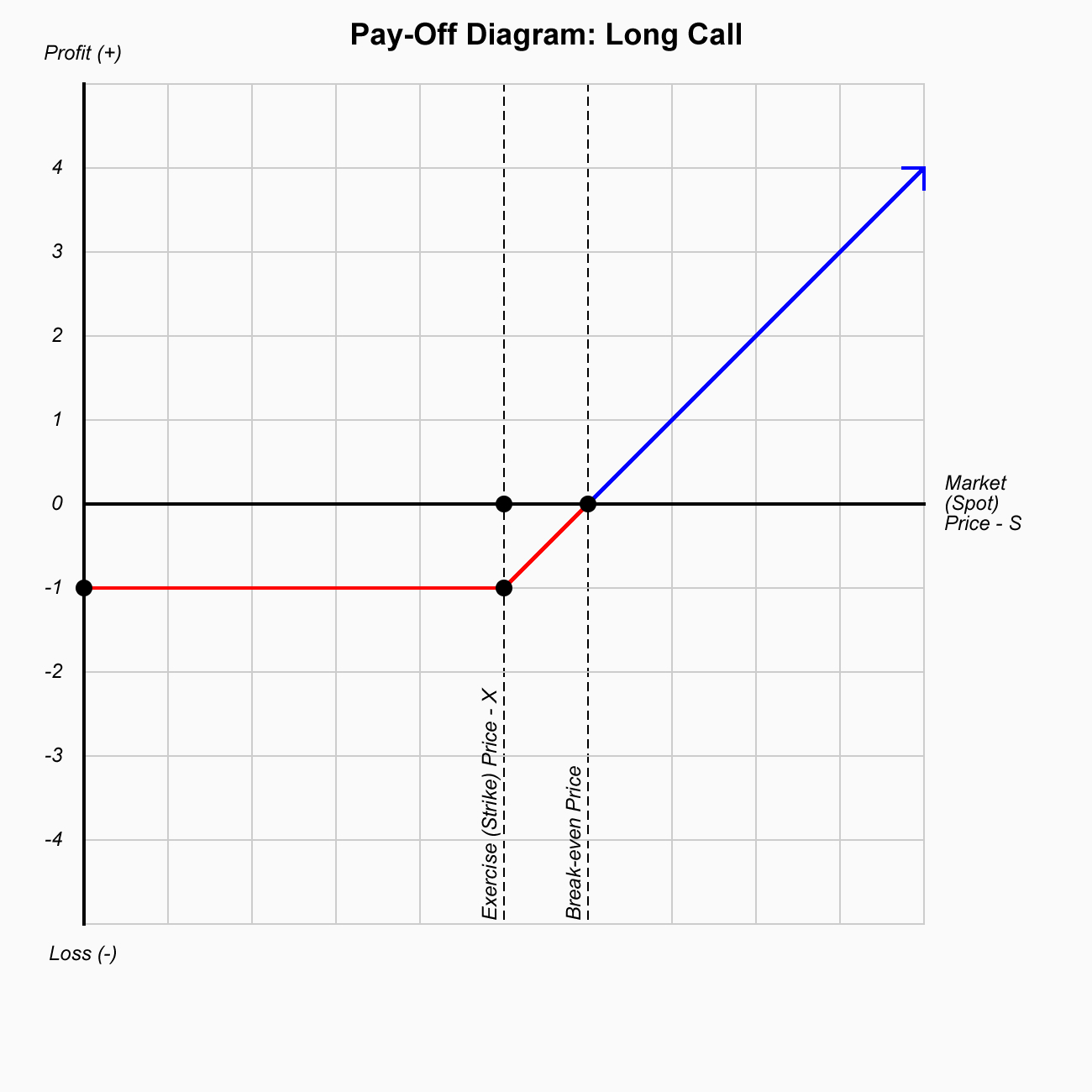
$$V = max(S-X, 0)-P $$
Long Call
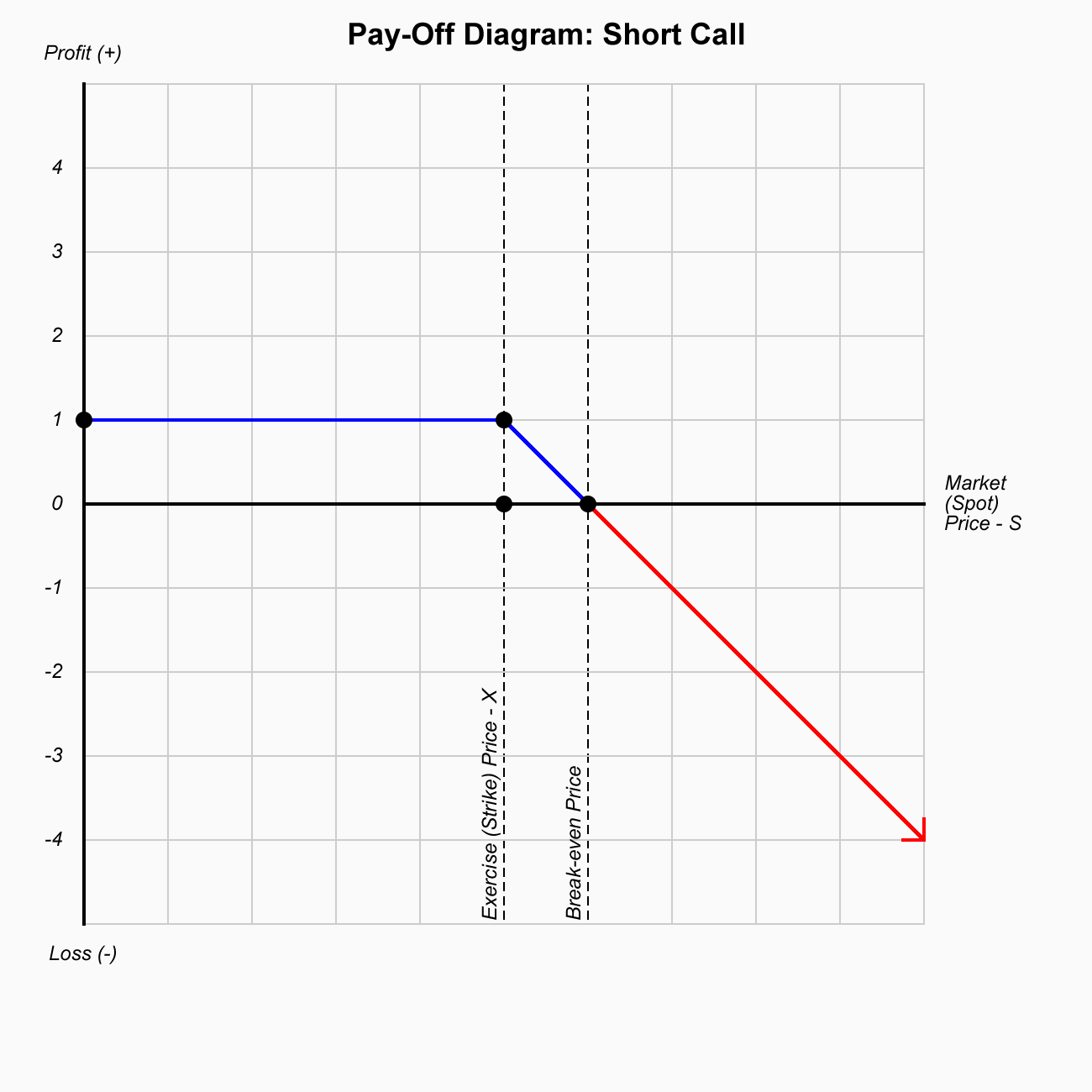
Short Call
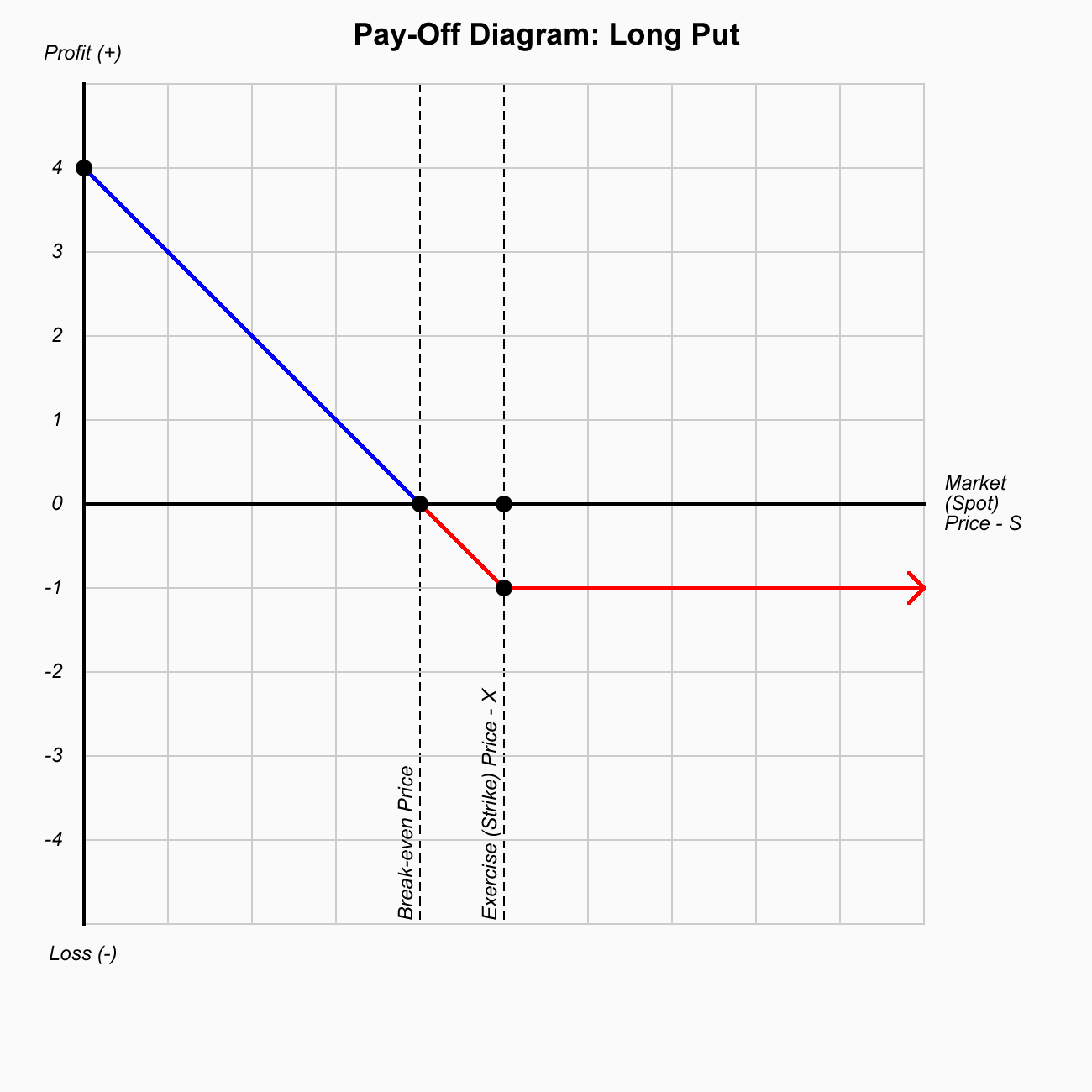
Long Put
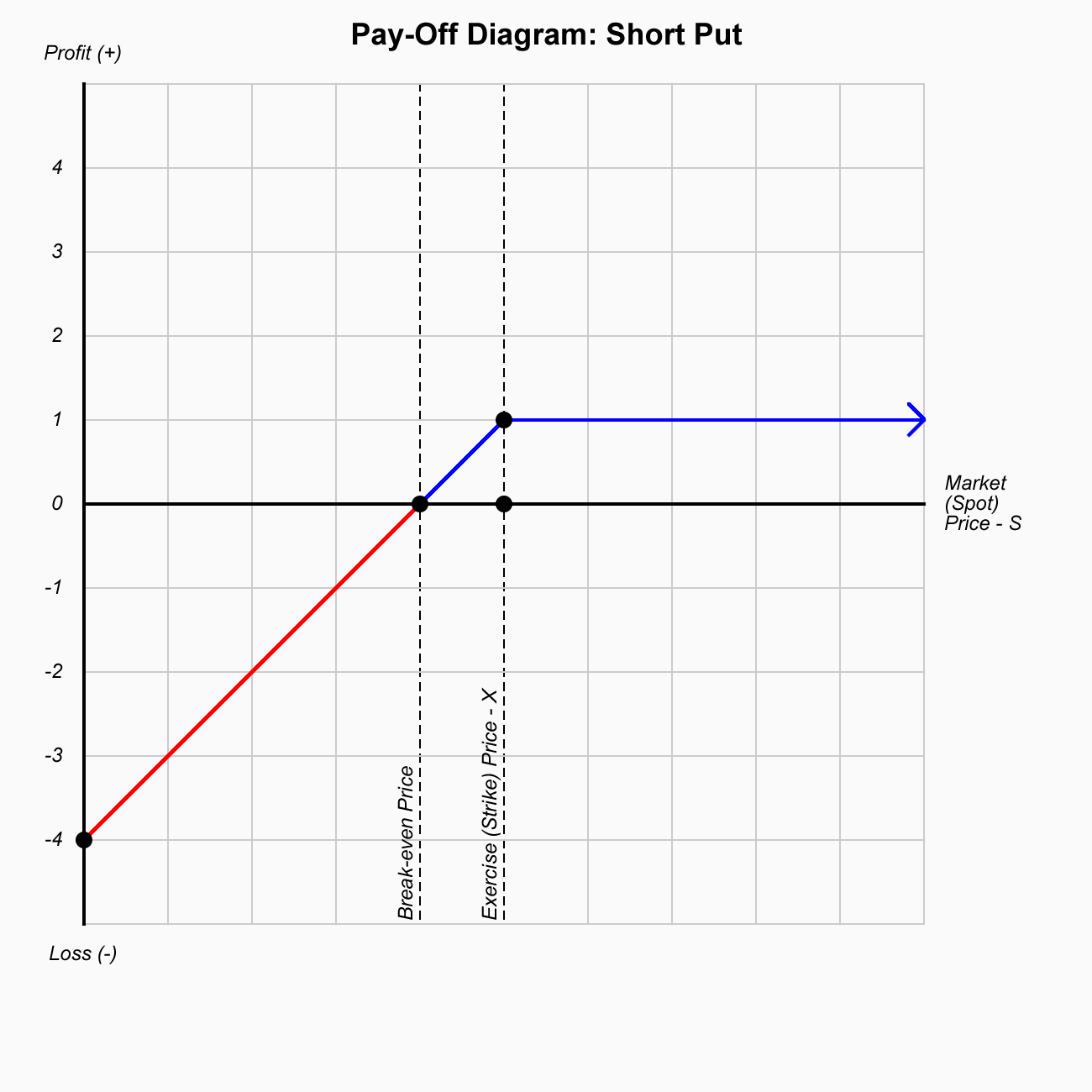
Short Put
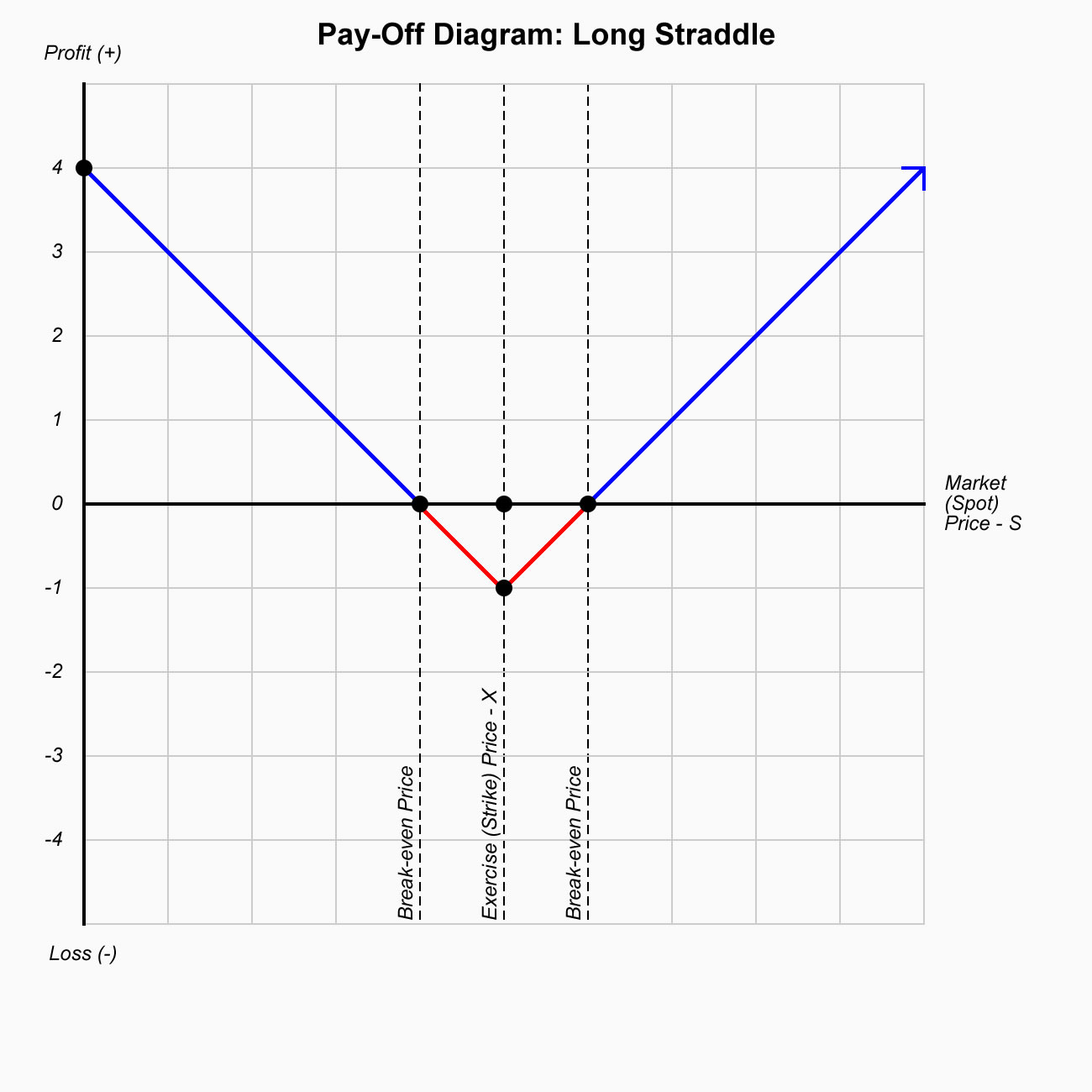
Long Straddle
- Strategy: Neutral
- Conditions: High Volatility
- Buy:
- Time Decay: Negative impact
- Break Even Points: Long Call – Premium, Long Call + Premium
- Max. Loss: Limited
- Max. Profit: Unlimited
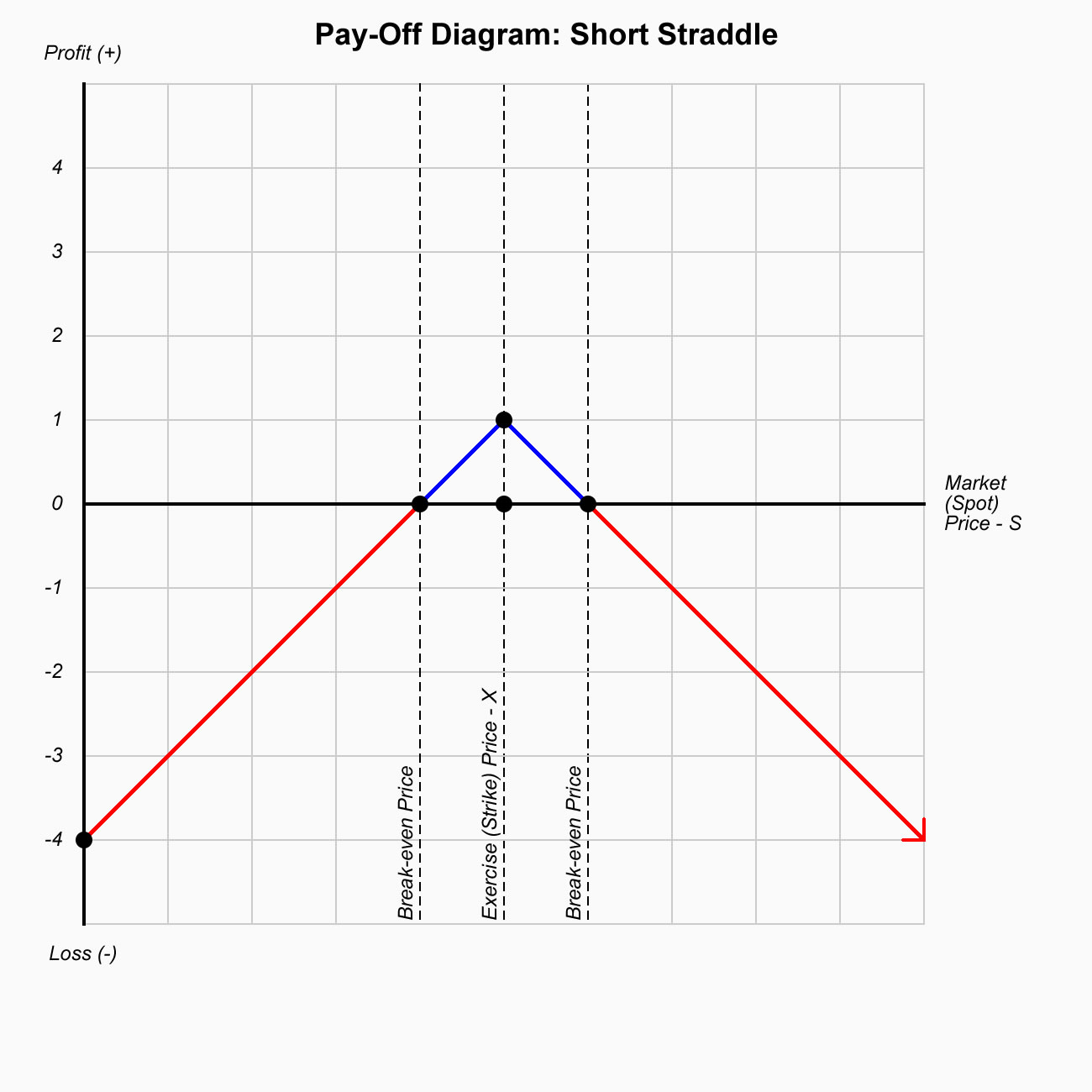
Short Straddle
- Strategy: Neutral
- Conditions: Low Volatility
- Sell:
- Time Decay:
- Break Even Points:
- Max. Loss: Unlmited
- Max. Profit: Limited
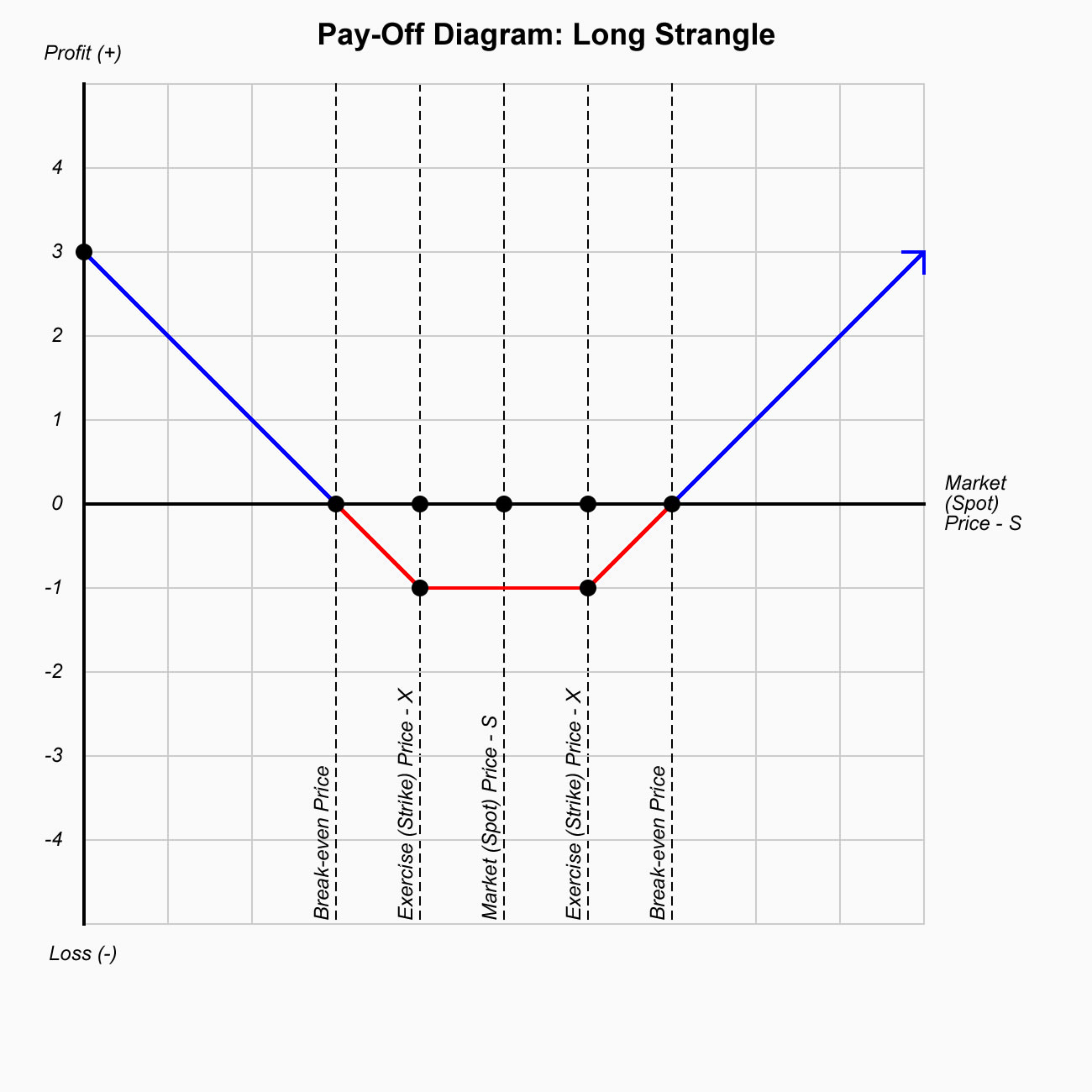
Long Strangle
With this strategy, a trader is looking for a major move; either up or down in the underlying stock before expiration. This market neutral strategy is specifically designed for high volatility conditions where stocks are swinging wildly back and forth.
- Strategy: Neutral
- Conditions: High Volatility
- Buy:
- Time Decay:
- Break Even Points:
- Max. Loss: Limited
- Max. Profit: Unlimited
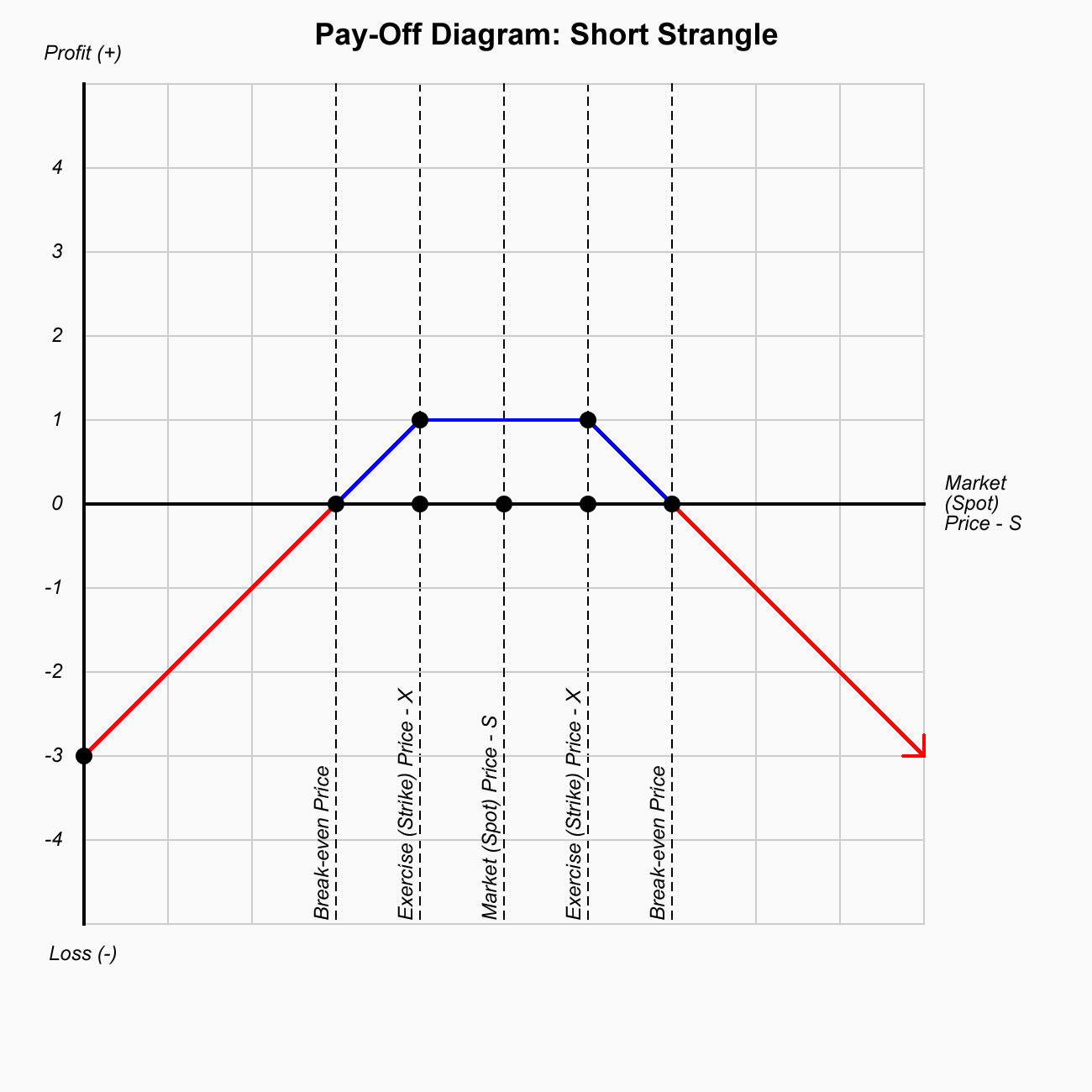
Short Strangle
- Strategy: Neutral
- Conditions: Low Volatility
- Sell:
- Time Decay:
- Break Even Points:
- Max. Loss: Unlimited
- Max. Profit: Limited
aaa









